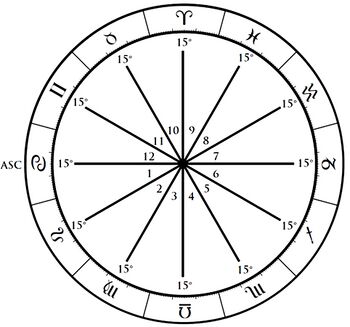
Equal house system
In an equal House System, all houses are 30 degrees in width. The Ascendant degree forms the cusp of the first house, and each subsequent house begins at the same degree.
The 10th house cusp therefore does not coincide with the MC but is square to the Ascendant and consequently the highest point of the zodiac above the horizon.
Although the Descendant will also form the 7th house cusp, the Medium Coeli (midheaven or MC) and Imum Coeli (IC) are embedded within a house; in most cases not necessarily in the 10th and 4th houses, respectively.
The equal house system has been in use since the time of antiquity.
In the example to the right the ascendant is located at 15 Cancer, and so the area from 15 Cancer to 15 Leo becomes the first house. Then the area from 15 Leo to 15 Virgo becomes the second house. 15 Virgo to 15 Libra becomes the third house, and so on.
Equal houses is one of the few systems of house division in which the degree of the MC floats freely in the top half of the chart, and does not mark the cusp or starting point of the 10th house. Instead, in this system the 10th house always begins exactly 90 degrees before the ascendant.
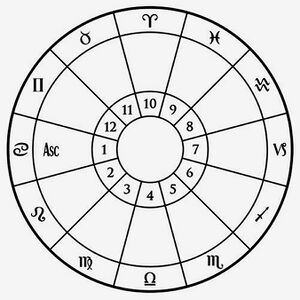
Whole Sign System
The equal house system is sometimes confused with whole sign houses, although the two approaches usually produce quite different results. The whole sign system is another type of equal house system, in which the ascendant sign, not the degree, determines the start of the first house, which is always set at 0 degrees of the sign.
Each sign follows in order, and is always 30 degreees in width. The Angles are typically embedded within a particular house and sign.
The whole sign house system was used in ancient Hellenistic and Vedic astrology (Jyotish), and it seems to have been the oldest and most popular form of house division in those traditions. Knowledge of this system was lost in the western tradition sometime during the Middle Ages, but then it was rediscovered in the 1980s and 1990s and became popular again in the first two decades of the 21st century.
See also
Weblinks
- Overview: Available house systems in Astrodienst's Extended Chart Selection
- The Whole Sign House System (Chris Brennan's Astrologyschool; 11min30)
- Wikipedia: Thema Mundi
Bibliography
- Robert Hand: Whole Sign Houses, the Oldest House System: An Ancient Method in Modern Application, ARHAT Publications, Reston, VA, 2000
- Robert Hand: Signs as Houses (Places) in Ancient Astrology, Culture and Cosmos, vol. 11, nos. 1 and 2, 2007, pp. 135–162
- James Holden: Ancient House Division, American Federation of Astrologers Journal of Research, vol. 1, no. 1 (August 1982), Tempe, AZ, pp. 19–29
Notes and References
- ↑ Illustration and main text of this article from Chris Brennan's Astrology Dictionary
- ↑ Houses according to the Thema Mundi
- ↑ Illustration from Chris Brennan